Category: Scheme Analysis
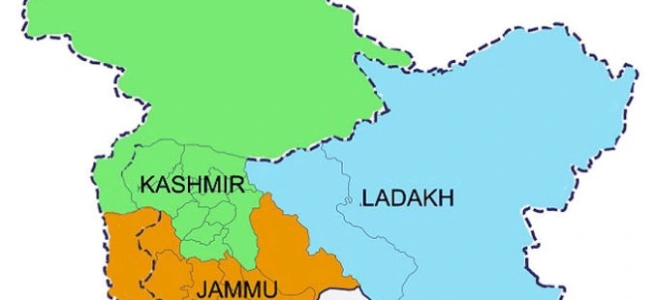
Analysis of The Constitution (Jammu and Kashmir) Scheduled Tribes Order (Amendment) Bill, 2023
The Constitution defines Scheduled Tribes under Article 366 (25) as tribes or tribal communities
deemed to be Scheduled Tribes under Article 342. Article 342 empowers the President, after
consultation with the Governor, to specify tribes or tribal communities as Scheduled Tribes
through public notification for a particular State or Union territory. Parliament, through law, can
include or exclude tribes from this list.1 The initial list of Scheduled Tribes was notified in 1950
and has been modified over time.
Analysis of The Constitution (Jammu and Kashmir) Scheduled Castes Order (Amendment) Bill, 2023
Scheduled Castes are defined in Article 366(24) of the Constitution as those castes, races, tribes,
or groups deemed under Article 341 to be Scheduled Castes (SC). Article 341 empowers the
President, in consultation with the Governor, to specify through public notification the castes,
races, tribes, or groups considered Scheduled Castes for a particular State or Union territory.
Additionally, Parliament has the authority to include or exclude any caste, race, tribe, or group
from the Scheduled Castes list through legislation, but once specified in a notification, it cannot
be altered by subsequent notifications.1
Background Note on The Jammu and Kashmir Reorganization (Amendment) Bill, 2023
The Jammu and Kashmir Reorganization (Amendment) Bill, 2023 aims to allocate 33 percent of
the seats in the Jammu and Kashmir assembly for women.1 This legislation, facilitating the
extension of the Women’s Reservation Law, is scheduled for introduction, consideration, and
passage during the Winter Session 2023.
Background Note on The Boilers Bill ,2023
Boiler is an essential tool for a number of industries including power plants, textile, feed, auto rice mills,
government factories, sugar and the pharmaceutical industry. The Indian Boilers Act 1923 is scheduled
to be re-enacted in the ongoing Winter Session 2023 as The Boilers Bill 2023. The former served as one
of the crucial legislations in India focusing on the safety aspects of steam boilers used in various
industrial settings. It was enacted in 1923 with a primary objective to ensure the safety of personnel
working with steam boilers and to prevent accidents that may result from using boilers.
Background Note on The National Capital Territory of Delhi Laws (Special Provisions) Second (Amendment) Bill, 2023
The population of the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi has been growing phenomenally over the years, including through migration. According to the 2011 Census, Delhi’s population stood at 11 million, while that of the NCT stood at 16.8 million; as per the Delhi Government’s Economic Survey (2022-2023), the population of Delhi now stands at 20.7 million (2021)2 . Further, migration added 2.83 Lakh people to Delhi’s population in 2021, which is more than double the number of residents contributed by births (with deaths accounted for)3.
The Central University (Amendment) Bill, 2023
The Government has proposed an amendment to the Central Universities Act of 2009. This new Bill titled, The Central Universities (Amendment) Bill, 2023, proposes the establishment of the Sammakka Sarakka Central Tribal University in Mulugu District, Telangana. This initiative is also in alignment with the provisions outlined in the Thirteenth Schedule of the Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act of 2014.1
Analysis of The Constitution (One Hundred and Twenty-Eighth Amendment) Bill, 2023
Analysis of The Constitution (One Hundred and Twenty-Eighth Amendment) Bill, 2023 To provide reservation to women in Lok Sabha, State Legislative Assemblies, and Legislative Assembly of NCT Delhi Background Even after 76 years of independence and equal political rights to all, India continues to witness a paltry representation of women in both the Parliament and […]
The National Cooperative University Bill, 2023
A cooperative university is an educational institution that operates under the principles of cooperation and
collective ownership. The efforts are being made for the establishment of a Cooperative University to firmly
deepen the foundations of the cooperative movement in the country.The Union Ministry of Cooperation is
planning to set up the world’s largest university for the cooperative sector that will award 9,600 degrees, 16,000
diplomas and 800,000 certificates annually by 2026-27. The plan is to award degrees for managerial positions,
diplomas for supervisory jobs and certificates for operational-level positions. The proposal involves setting up
sector-specific schools for dairy, fishery, rural credit and cooperative credit among others at an investment of
around ₹750 crore over a three-year period.
The Drugs, Medical Devices, and Cosmetics Bill, 2023
India’s pharmaceutical industry, valued at $41 billion, stands as one of the largest in the
world. Over the years, it has played a crucial role in offering cost-effective alternatives
to Western products, particularly benefiting impoverished and developing countries.1
The recent deaths of at least 66 children in the Gambia, attributed to cough syrups
produced by Haryana-based Pharmaceuticals, have brought attention to the
deficiencies in India’s drug regulatory system.